
Watch the interview with Dr. Enrico Storti, Anesthesia and ICU Director/Unit Coordinator of the Emergency Department at Maggiore Hospital, from the frontlines of the COVID-19 pandemic in Lodi, Italy.
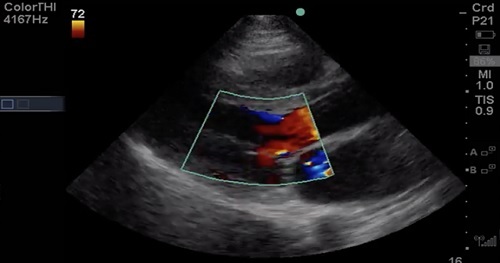
This course will outline a 4-step process for evaluating valve function.
Step 1: 2D evaluation of the valve (eyeball method)
Step 2: Assess the valve with color Doppler for Mitral Regurgitation (MR) or Aortic Regurgitation (AR)
Step 3: Assign relative importance of lesion
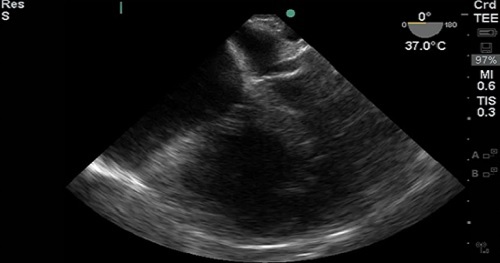
This course will compare Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) and Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE), outline clinical questions with point-of-care TEE, describe how to get started with TEE (politics, cost, logistics), discuss safety and training, review a suggested TEE protocol, and give several case examples using TEE.
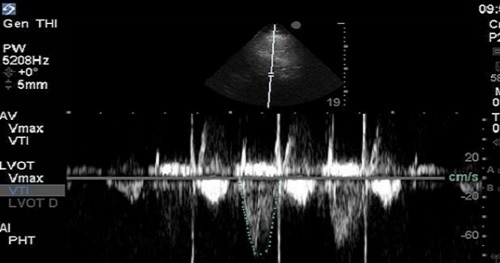
Determination of Stroke Volume (SV) is perhaps the most essential of all the “advanced” techniques for point-of-care echocardiography. It’s considered advanced, because it relies on quantitative spectral Doppler techniques, which are not routinely part of the core point-of-care echocardiography curricula offered for most specialties at the time of this publication. This technique is the most practical and intuitive gateway to hemodynamic understanding of echocardiography and is a powerful adjunct in the assessment of Left Ventricular (LV) function.
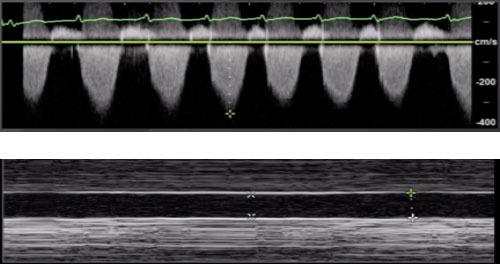
There are a number of different data points that can be collected that inform us of the function and loading conditions of the Right Ventricle (RV): Shape and size of the RV, Inferior Vena Cava (IVC), Tricuspid Angular Plane Systolic Excursion (TAPSE), and Right Ventricular Systolic Pressure (RVSP).